By now, you’ve probably heard about the growing use of radio frequency identification, or RFID. Supply chain businesses, including those in Asia and Latin America (but not Europe), are using it to improve productivity and increase profits. There are many companies who question the benefits and technology behind RFID systems. Many people are uncertain about how RFID systems will work in their warehouse or distribution center. If you’ve ever wondered what RFID is—and if it can benefit your business—KingTop is here to help! Follow this guide for an explanation of what RFID means, what its capabilities are—and why your company might want to use one!
What is RFID technology?
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a technology that involves using low-power radio waves to automatically identify objects. Data is transferred and stored by a system consisting of tags, antennas, readers/writers, transceivers and microcontrollers. RFID technology is used in many industries—from retail to manufacturing to healthcare and logistics.
The technology enables businesses to track items quickly and efficiently with a low cost of implementation. RFID is a technology used to identify, locate and track items. The radio waves emitted from an RFID tag are read by an antenna, which sends the data to a reader or sensor. The reader then processes this information and sends it over a network to an application that uses that information for various purposes. The technology is primarily used to track inventory, but it can also be used to track people or pets. It’s often found in the form of microchips embedded in credit cards and passports.
How does RFID work?
Unlike barcode scanners, which read optical reflections from printed labels, RFID scanners use low-power radio frequencies to “read” data stored on tagged items. In a warehouse or distribution center, radio-frequency identification technology is used to automate data collection. The transceiver reads and transmits information from an attached tag by means of radio waves. The identification information is transmitted from the tag's embedded computer chip to an RFID reader. The reader is a small device that can be mounted on the wall or placed on a countertop. It has an antenna that transmits and receives radio signals. The reader then decodes the data from the tag and displays it as text on its screen. The reader also has a keyboard that allows a user to enter information into the system. For example, if an item is scanned and its ID number is not found in the database, the operator can type in the number manually. The RFID reader can then be used to enter information into the database. The system can also be programmed so that when a tag is scanned, its ID number is automatically entered into a database and the item's location is tracked.
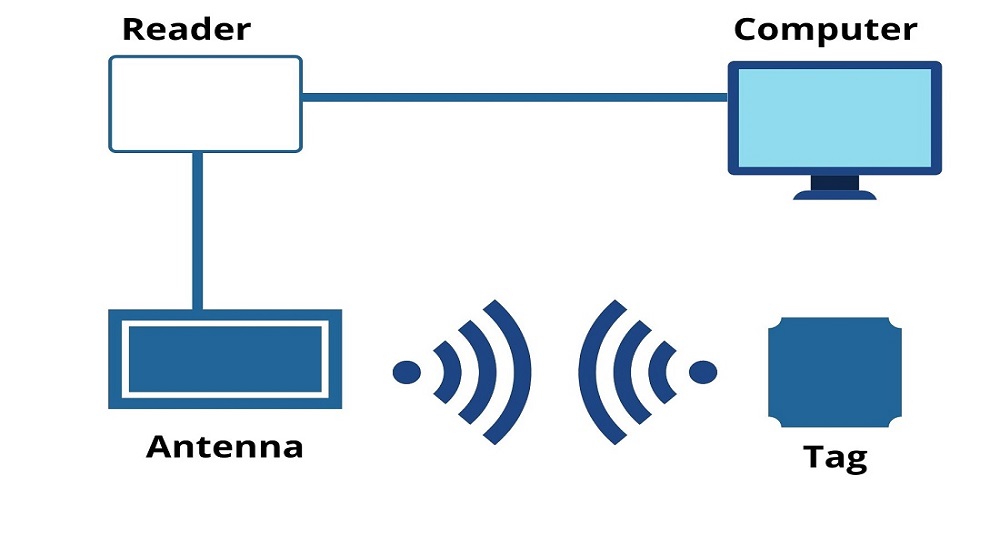
How does RFID scanning differ from barcode technology?
RFID is a technology that uses radio waves to read and identify objects. It’s a form of automatic identification that doesn’t require the user to scan a barcode or enter any information manually. RFID systems can be used to track, monitor and manage inventory, as well as provide security features like access control and anti-theft protection. RFID systems use a device called an RFID reader to read the tags attached to objects. The reader sends out radio waves that are received by RFID tags and used to identify the object’s location, movement or status. There are two different kinds of RFID systems: active and passive. In an active system, each tag has an embedded battery and transmitter that transmits back data about its location when it comes within range of an antenna. This is the most common type of RFID system, and it’s often used in supply chain management. Active systems are more expensive than passive ones because they require batteries and transmitters to be built into each tag. Passive systems don’t need these components because they receive power from the reader itself.
Barcodes and radio-frequency identification (RFID) devices both have functionalities similar to those of traditional barcodes, but one difference between them is that the human intervention required for RFID makes it less popular than its predecessor. This refers to the distance between an operator and the item being scanned — in other words, whether or not they are close enough to see it. In order to obtain a barcode read, operators must place their handheld scanners at an angle where they can view the entire code. Operators can collect data using RFID technology so long as the tag is within range. Employees can collect data for any item within the read range without having to physically move from shelf to shelf. RFID can also read multiple items at once, which makes it a valuable tool for companies looking to make their operations more efficient. If you need a RFID scanner, you can seek reliable RFID scanner supplier.
What are the advantages of using RFID?
Supply chain businesses can monitor their assets' location in real time with radio frequency identification (RFID) tags. RFID can help businesses reduce the costs that are associated with manufacturing, distribution and inventory management by eliminating labor-intensive inventory-tracking processes (which require human intervention) and increasing visibility of items. RFID can help you collect data more efficiently, freeing your employees to focus on the tasks that are most important—like customer service and shipping.
Automated data collection systems can significantly reduce the time spent gathering and analyzing information, making it possible to report on business trends more quickly. Because of these factors, companies can reduce their labor costs and increase throughput—all while reducing inventory carrying costs. Additionally, with more precise delivery methods customers will be happier when their orders are delivered on time.

For more information, please contact KingTop. You can choose a suitable product from KingTop, a RFID scanner supplier. We’re always happy to help!


 French
French German
German Arabic
Arabic Italian
Italian Spanish
Spanish Japanese
Japanese Persian
Persian Korean
Korean Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified)









